What are Capsule Networks ?
Problem with Pooling Layers
It’s important to note that pooling operations such as Max pooling or Average pooling do throw away some image information. That is, they discard pixel information in order to get a smaller, feature-level representation of an image. This works quite well in tasks like image classification, but it can cause some issues.
- A fake image with 3 eyes or a nose placed on top of eyes still recognize the image as a facial image by distilling an image into a feature-level representation.
We know its a fake image right? But, how does a neural network understands such information?
So, there has been research into classification methods that do not discard spatial information (as in the pooling layers), and instead learn to spatial relationships between parts (like between eyes, nose, and mouth).
One such method, for learning spatial relationships between parts, is the capsule network.
Capsule Networks
Capsule Networks provide a way to detect parts of objects in an image and represent spatial relationships between those parts. This means that capsule networks are able to recognize the same object, like a face, in a variety of different poses and with the typical number of features (eyes, nose , mouth) even if they have not seen that pose in training data.
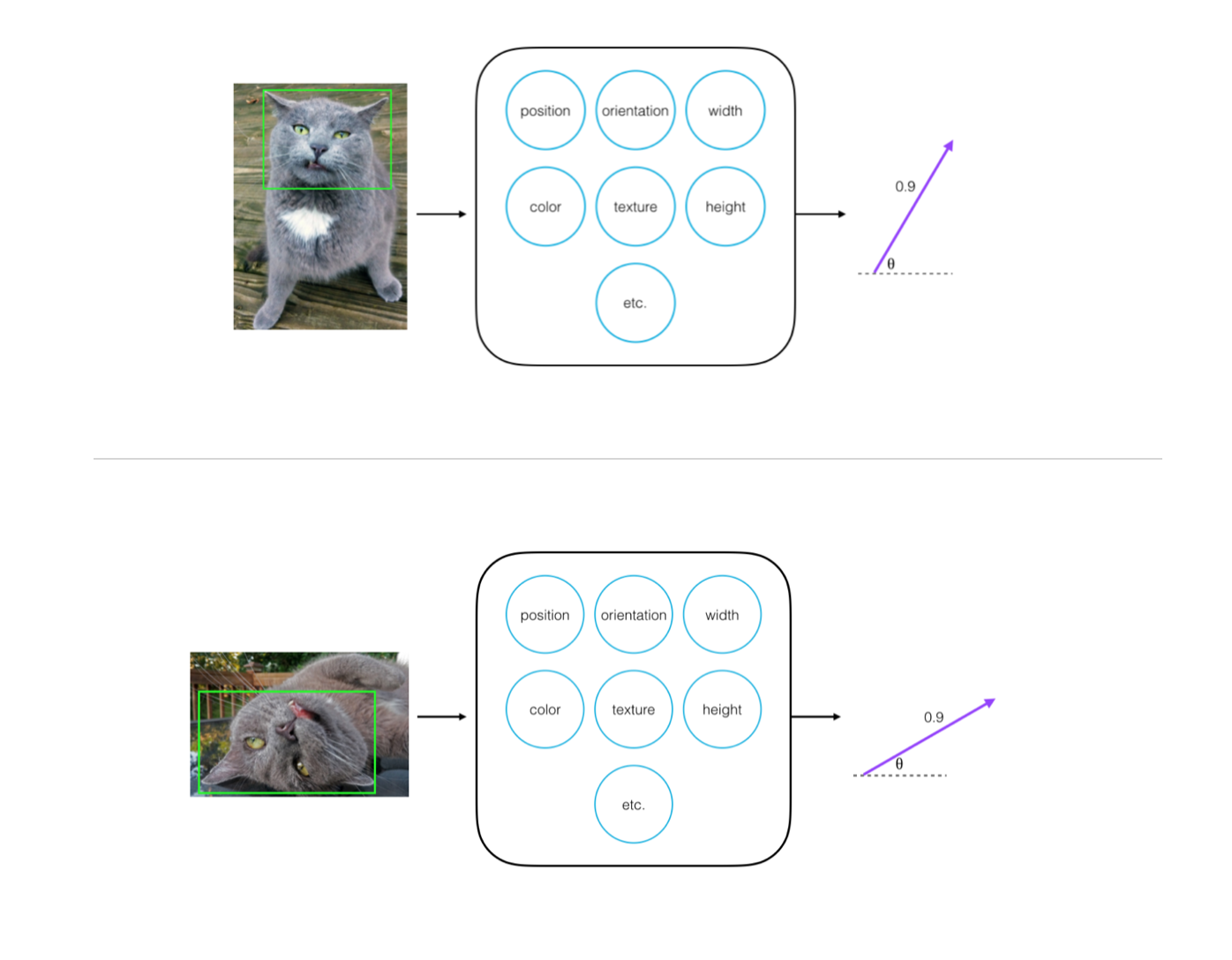
- Each neuron in a capsule represents various properties of a particular image part; properties like a parts color, width, etc.
- Every capsule outputs a vector, which has some magnitude and orientation.
- Capsules have a hierarchy between child and parent capsules and use dynamic routing to find the strongest connections between the output of one capsule and the inputs of the next layer of capsules.
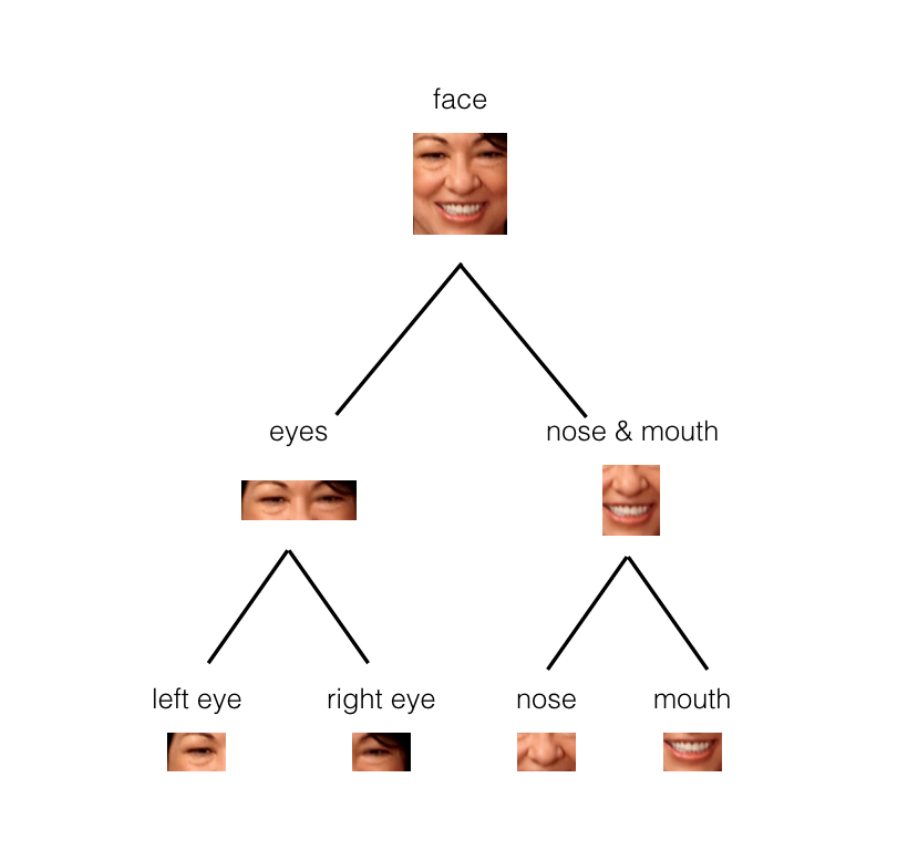
In the example above, you can see how the parts of a face (eyes, nose, mouth, etc.) might be recognized in leaf nodes and then combined to form a more complete face part in parent nodes.
- Magnitude (m) = the probability that a part exists; a value between 0 and 1.
- Orientation (theta) = the state of the part properties.
These output vectors allow us to do some powerful routing math to build up a parse tree that recognizes whole objects as comprised of several, smaller parts!
The magnitude is a special part property that should stay very high even when an object is in a different orientation, as shown below.
Model Architecture
The Capsule Network is made of two main parts:
- A convolutional encoder
- A fully-connected, linear decoder
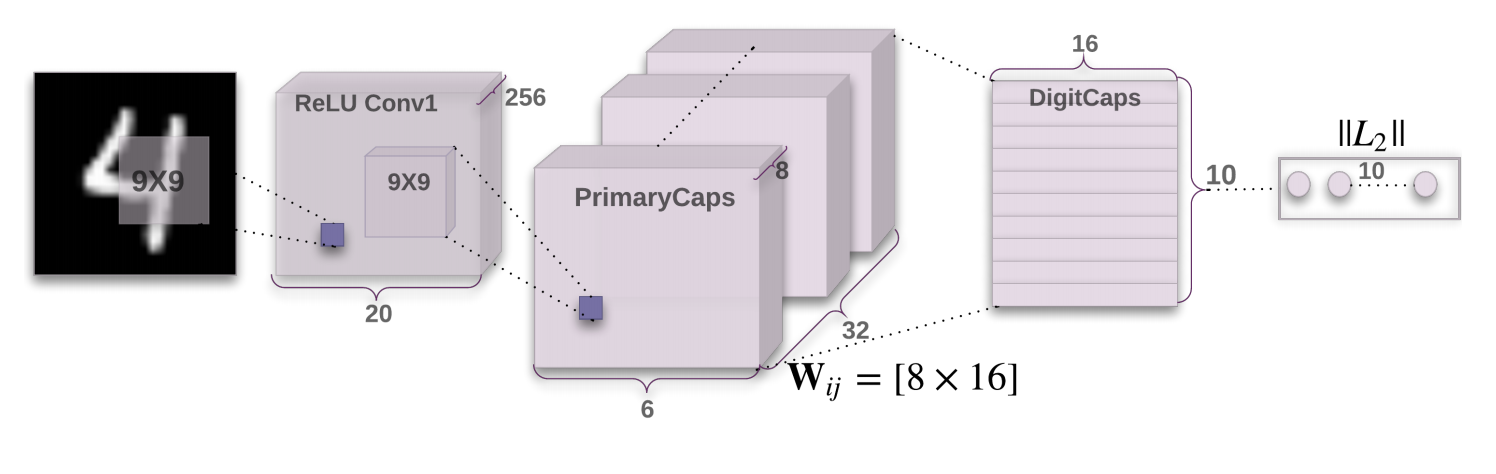
The above image was taken from the original Capsule Network paper (Hinton et. al.).
Resources & Acknowledgements
https://github.com/cezannec/capsule_net_pytorch
https://github.com/udacity/deep-learning-v2-pytorch/blob/master/README.md
